Glass Spacer Testing Report: Cork vs. EVA Foam Pads (Weidu Lab)
Why Glass Spacers Matter in the Glass Industry
A small glass spacer plays the role of an essential “protector” in the glass industry. It ensures safety and protection throughout the entire process from factory to installation. There are many types of glass spacers available, and their performance and surface residue risk differ depending on the material, function, and design.
Common Problems Caused by Low-Quality Spacers
Poor-quality spacers often leave oil stains, glue marks, or cause scratches due to friction, leading to serious issues. In this test, Weidu Lab selected three electrostatic adsorption spacers—Cork, Black EVA foam, and White EVA foam—to evaluate their compression performance and residue risks.
Types of Glass Spacers Selected for Testing
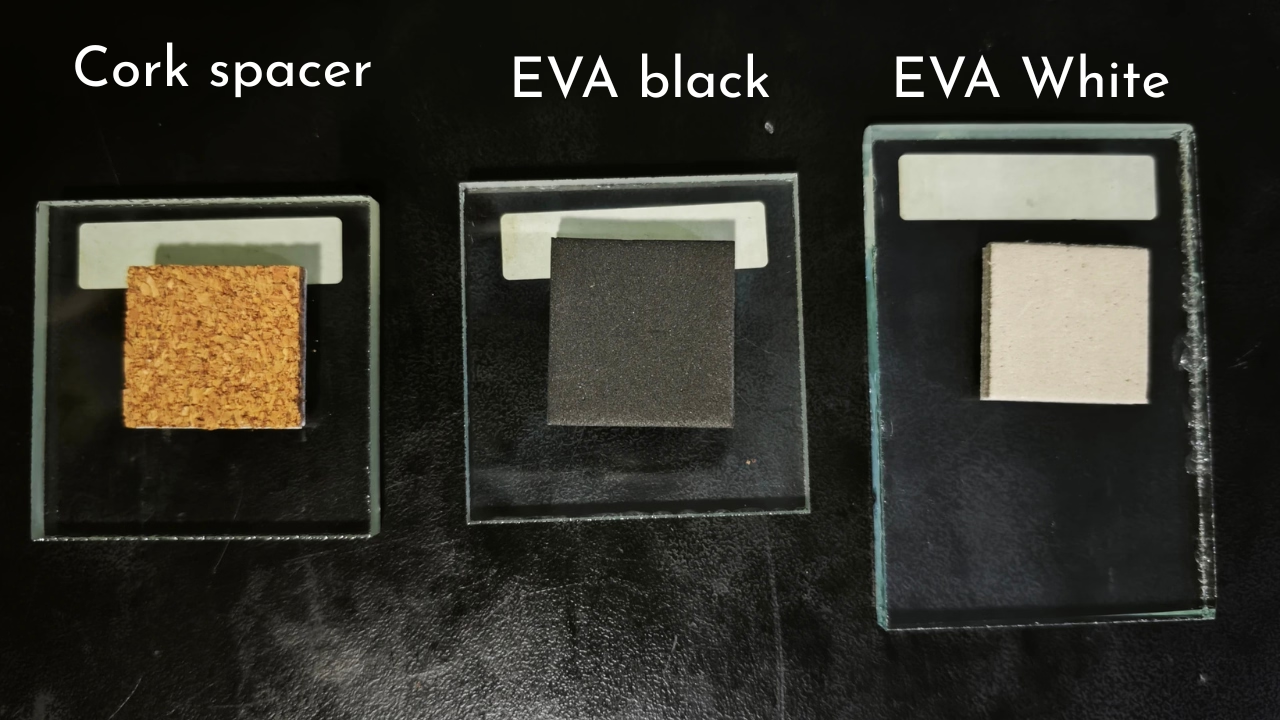
| Type | Thickness | Size | Shore C Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cork Pad | 4mm | 23×23mm | 70–75° |
| EVA Foam (Black) | 4mm | 28×28mm | 75–80° |
| EVA Foam (White) | 4mm | 23×23mm | 70–75° |
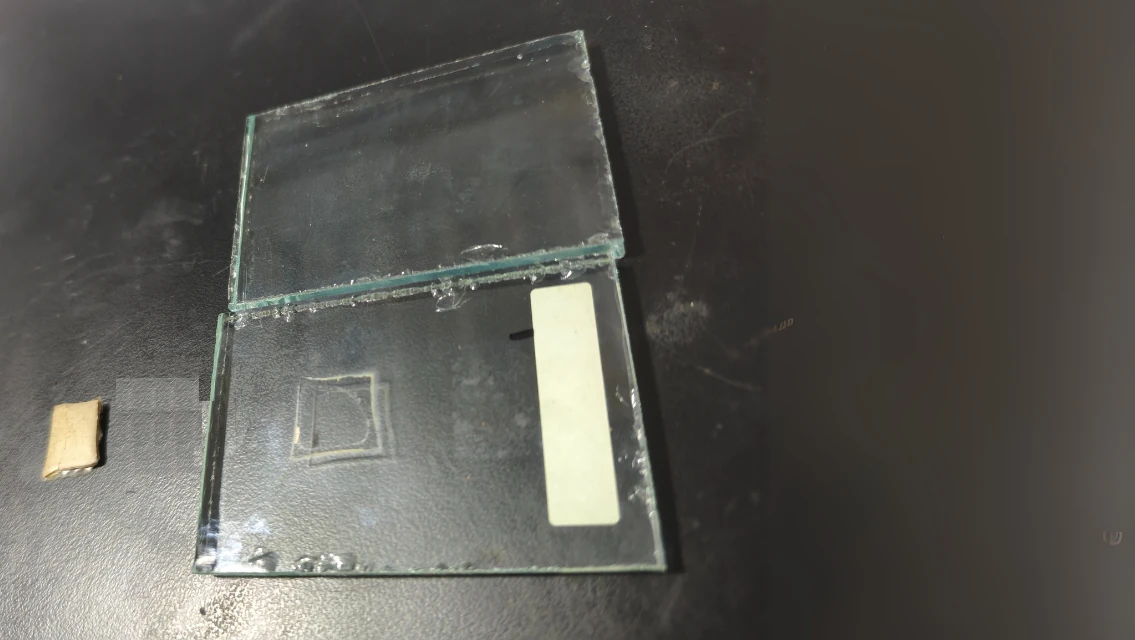
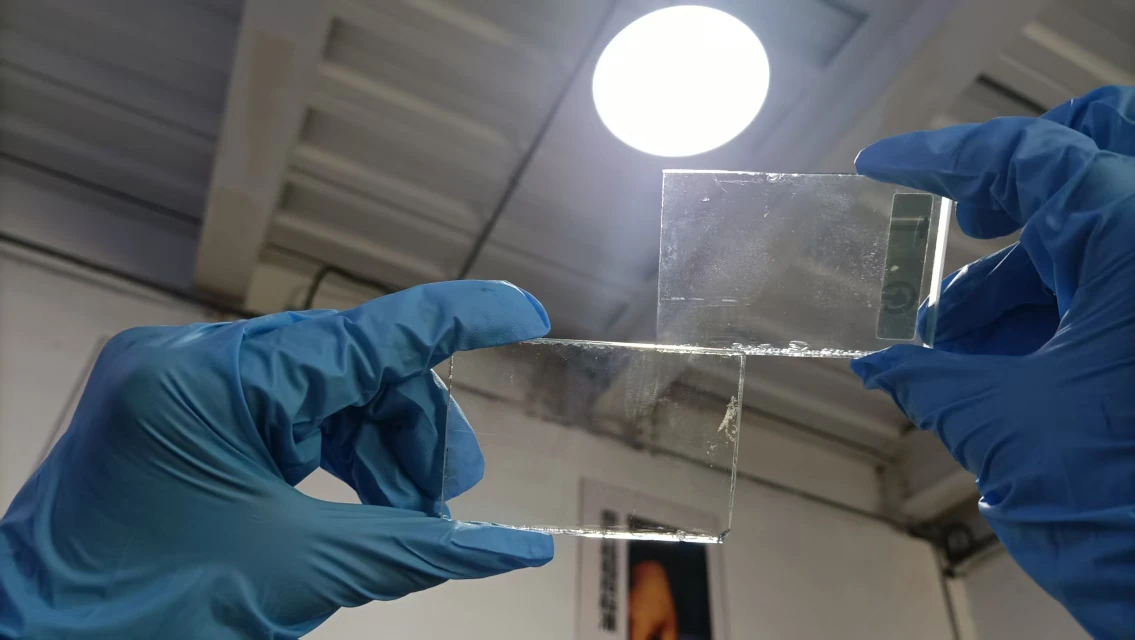
High-Temperature Compression Test (150°C for 3 Hours)
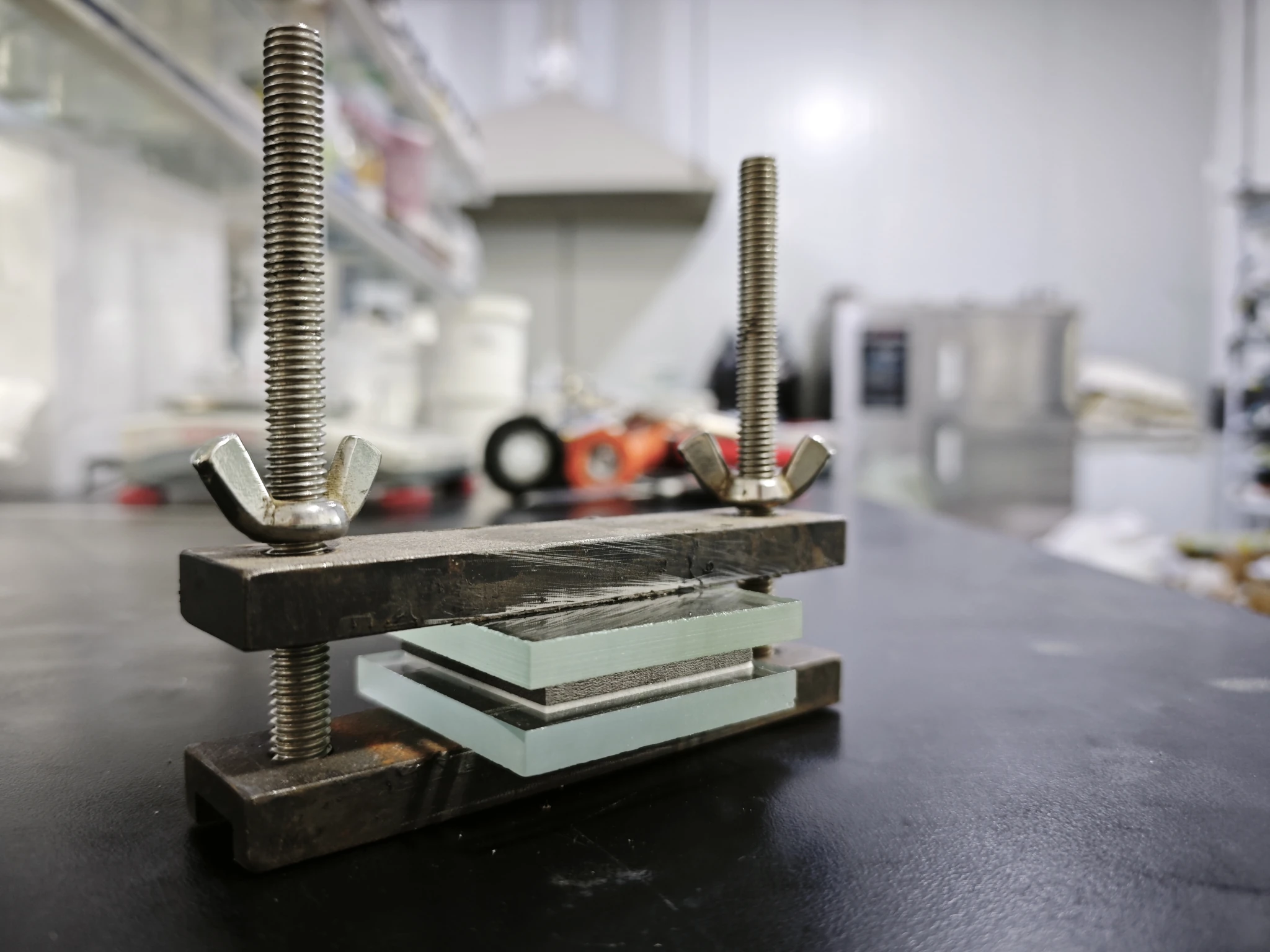

The purpose of this test was to simulate extreme heat conditions and evaluate the stability and residue left on the glass surface after exposure.
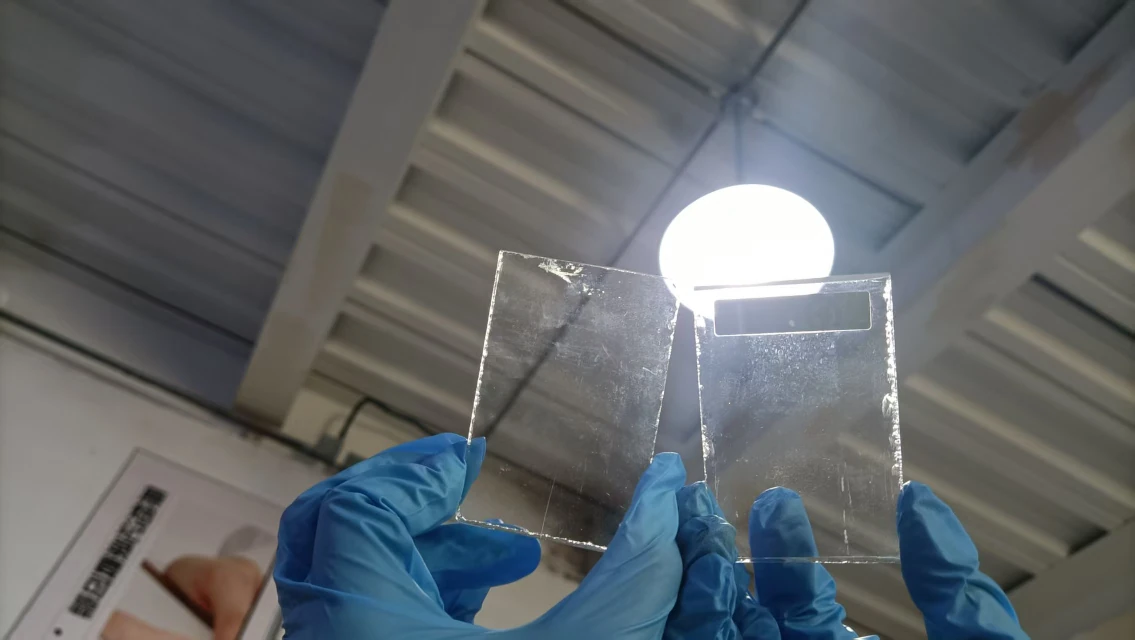

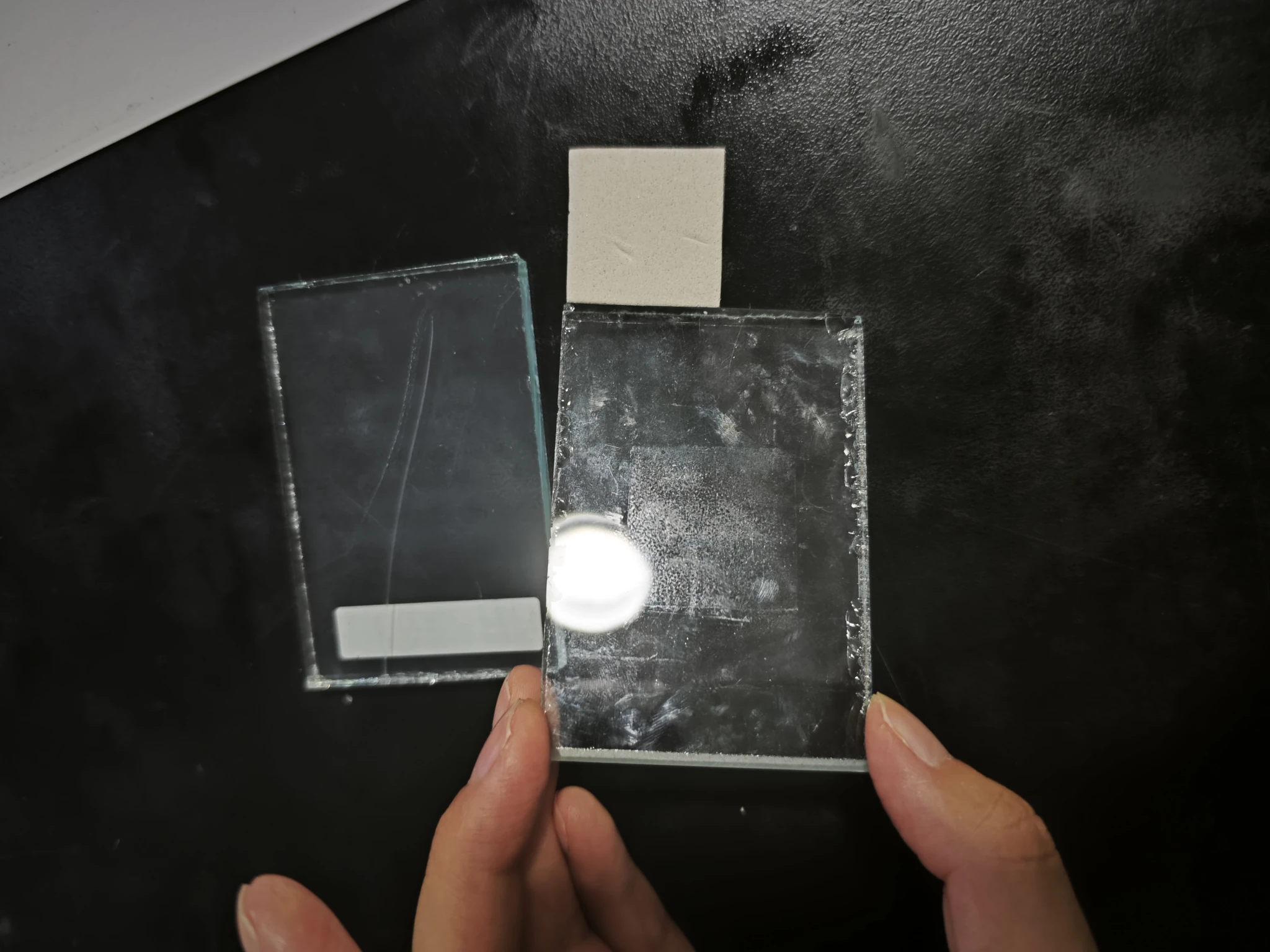
Long-Term Compression Test at Room Temperature (4 Days, 34°C)
This test simulated glass being stacked or transported for an extended period. The spacers were clamped between glass panels for four days at 34°C, and impressions and residues were recorded.
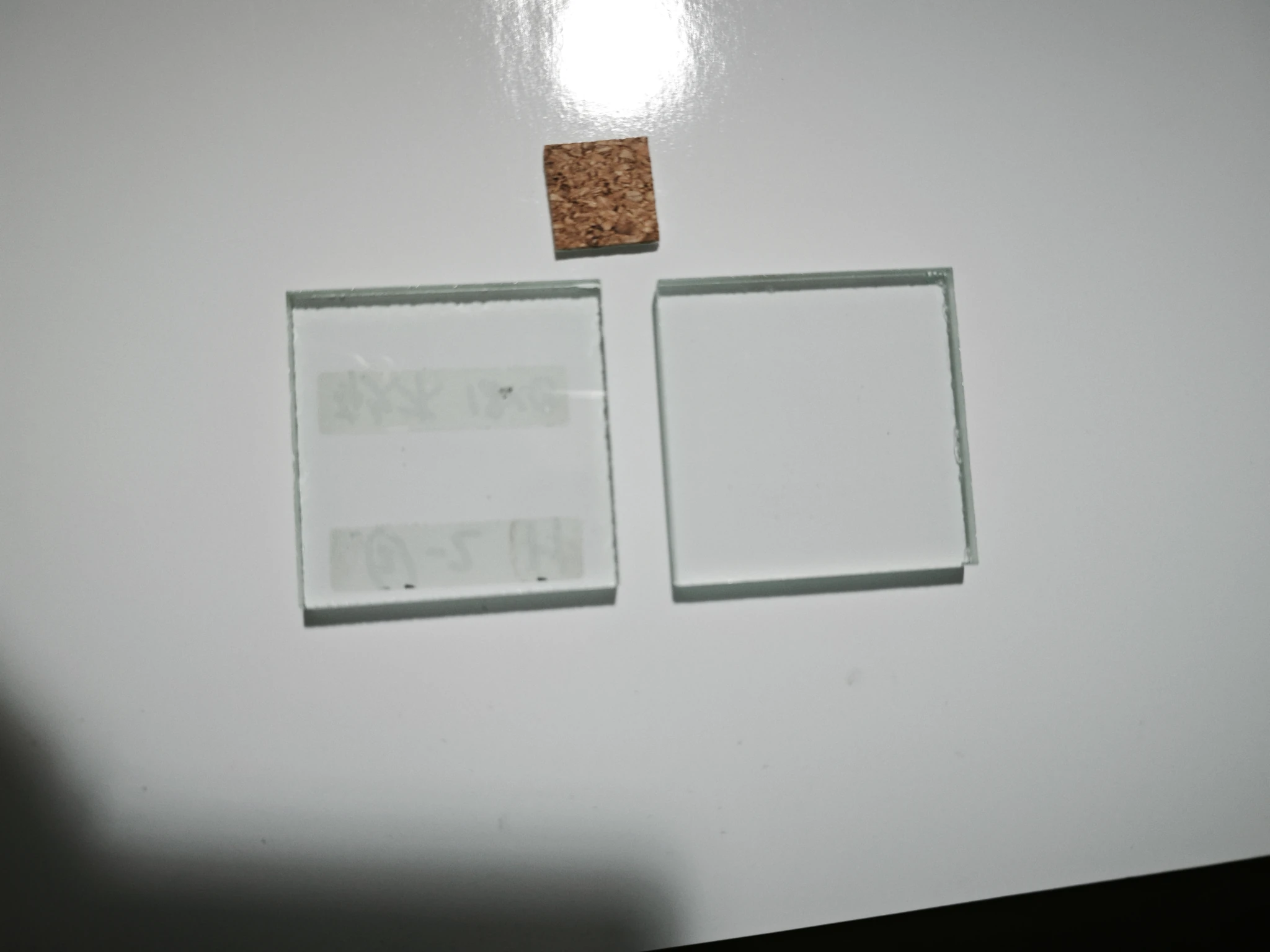


Analysis of Test Results
Electrostatic adsorption spacers contain a middle glue layer. Under heat and long-term pressure, plasticizers or oily components can migrate to the glass surface, leaving stains. Low-quality glue has poor temperature resistance and higher migration risk. Cork pads, being natural and eco-friendly, showed superior compression resistance. Black EVA, with carbon black, has higher resistance than white EVA, which showed poor temperature stability and high compression rates.
Choosing the Right Glass Spacer for Different Scenarios
- High-quality spacers use eco-friendly glue with better resistance to temperature and migration.
- Harder materials perform better under load.
- Choose spacers according to the environment: cork for high-temperature indoor use, EVA for outdoor waterproofing needs.
- Match spacer size and quantity to glass dimensions.
Looking for high-quality EVA glass spacer pads? Check out our EVA Glass Separator Pads product page for detailed specifications and options.
Usage Recommendations
- Workers should wear dustproof gloves to avoid fingerprints transferring to glass.
- Wait until glass cools before using spacers.
- Spacers are only for short-term isolation, not long-term adhesion.
How to Clean Spacer Residue?
If stains remain, use anhydrous or medical alcohol with a sponge or soft cloth to wipe repeatedly, then rinse with water.
FAQ
1. Which glass spacer is best for high-temperature environments?
Cork pads are the best choice as they withstand heat and maintain compression resistance.
2. Why does white EVA foam show more residue?
White EVA foam has lower hardness, looser pores, and weaker heat resistance, leading to higher compression rates and oil migration.
3. Can EVA pads be used for Low-E glass?
Low-E glass requires dedicated spacers to avoid damaging its special coating. Cork or specialized spacers are recommended.
4. How to reduce the risk of glue migration?
Choose spacers made with eco-friendly adhesives and avoid long-term pressure or exposure to heat and sunlight.
5. Are spacers reusable?
No, spacers are designed for one-time use. Reusing them increases the risk of residue and reduced performance.


